In what Lawrence Livermore Nationwide Lab stated is “a considerable milestone for supercomputing-aided drug design,” LLNL and BridgeBio Oncology Therapeutics right now introduced medical trials have begun for a first-in-class medicine that targets particular genetic mutations implicated in lots of forms of most cancers.
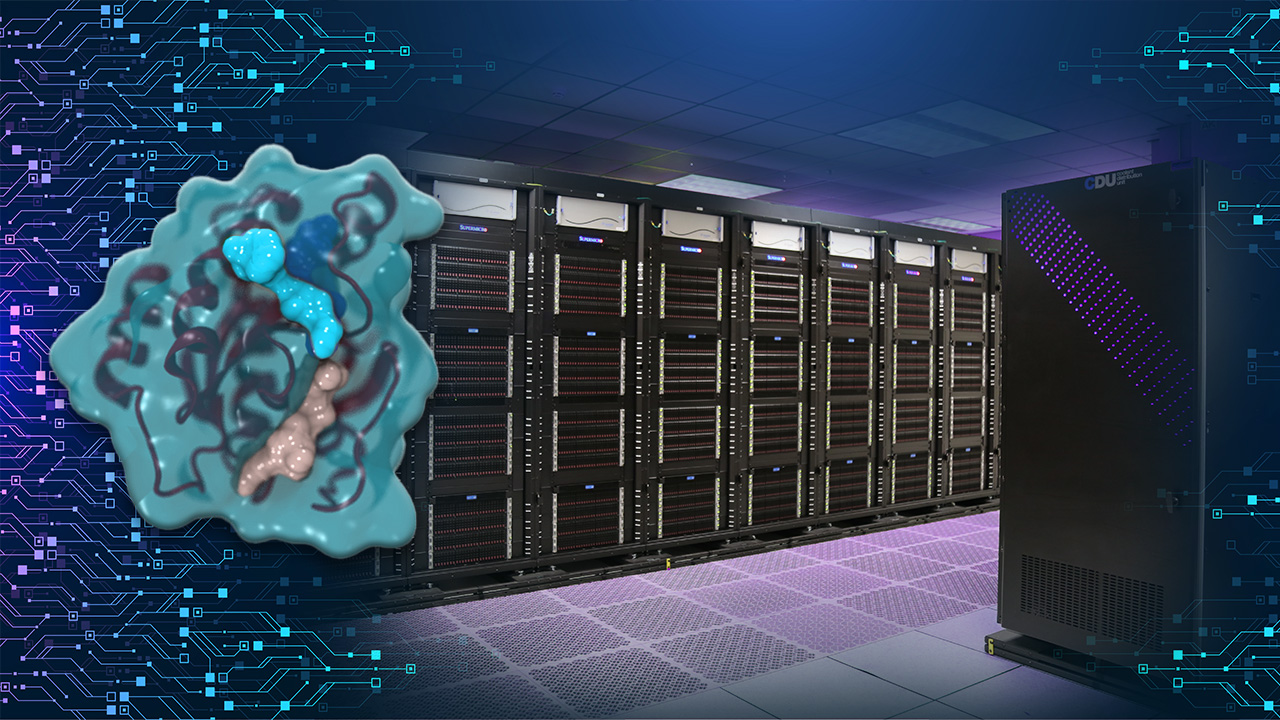
The drug discovery work was powered by LLNL supercomputers Ruby (proven right here), Quartz and Lassen. Of the three, Lassen is essentially the most highly effective, ranked 57th on the latest Top500 record of the world’s strongest supercomputers. It’s powered by IBM POWER and Nvidia processors and was put in at Livermore in 2018. The CPU-powered Ruby cluster was put in on the lab in 2020 by Intel, Supermicro and Cornelis Networks and initially supported the lab’s COVID-19 analysis. The Quartz system was put in at Livermore in 2016.
Funded by NNSA’s Superior Simulation and Computing (ASC) program, the Laboratory’s Multi-programmatic and Institutional Computing (M&IC) program and the Coronavirus Support, Reduction and Financial Safety (CARES) Act, the 6 petaFLOP peak, Intel Xeon Platinum-based cluster can be used for unclassified programmatic work in help of NNSA’s stockpile stewardship mission, LLNL open science and the seek for therapeutic medicine and designer antibodies towards SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.

Felice Lightstone, LLNL
The event of the brand new drug — BBO-8520 — is the results of collaboration amongst LLNL, BridgeBio and the Nationwide Most cancers Institute (NCI)’s RAS Initiative on the Frederick Nationwide Laboratory for Most cancers Analysis (FNL). In a primary for a Division of Vitality (DOE) nationwide laboratory, the drug was found by means of DOE HPC assets mixed with an LLNL-developed platform integrating synthetic intelligence and conventional physics-based drug discovery, and partnership with the FNL and NCI.
The drug candidate has proven promise in laboratory testing for inhibiting mutations of KRAS proteins linked to about 30 % of all cancers — targets lengthy thought of “undruggable” by most cancers researchers. LLNL stated “the achievement supplies hope for broad affect on most cancers sufferers whose tumors harbor vulnerable KRAS mutations. This means {that a} computational/AI drug design method may unlock new insights into the illness and the way forward for most cancers therapy.”
“For the DOE complicated, that is the primary true instance that prime efficiency computing can speed up drug discovery, which is strengthened by making it to human trials,” stated LLNL Biochemical and Biophysical Methods Group Chief Felice Lightstone, principal investigator for the challenge. “Passing FDA clearance to get to human trials already says that the FDA has regarded on the design, and we’ve met all the factors to have a real-world utility. Not solely that, however we’re taking our primary analysis in excessive efficiency computing and changing it to an utility that trade can discover helpful — this can be a true milestone.”
Livermore Lab stated that after simply three years of improvement, because of a legacy of scientific experience in small molecule analysis, LLNL’s HPC capabilities and the Livermore Pc-Aided Drug Discovery (LCADD) platform, the U.S. Meals and Drug Administration (FDA) cleared BBO-8520 for human trials in Dec. 2023. The trial will concentrate on sufferers with KRASG12C mutant non-small cell lung most cancers and can check the novel inhibitor for security and efficacy.
Whereas a typical drug discovery program synthesizes many hundreds of promising compounds to design and develop a drug, the crew behind this analysis initially synthesized just a few hundred compounds to find BBO-8520 — utilizing the AI- and physics-based LCADD platform to slim down the variety of potential profitable small molecules for synthesis. With hundreds of compounds modeled in silico, the crew synthesized about 850 compounds for the complete challenge.
The joint effort stems from Cooperative Analysis and Growth Agreements (CRADAs) between LLNL and BridgeBio Oncology Therapeutics and between BridgeBio and FNL, aimed toward advancing discovery of novel RAS inhibitors for the therapy of most cancers. The CRADAs introduced the three establishments collectively to deal with essentially the most difficult points of most cancers remedy: the lengthy timeframe to carry a drug to market and the excessive fee of failure for promising drug candidates. LLNL additionally noticed the issue as an essential use case for superior computing. Within the coming years, LLNL and BridgeBio will proceed to hunt new compounds for different targets recognized by the RAS Initiative, experimentally testing and validating these compounds, analyzing interactions between compounds and targets and optimizing current compounds.
“It is a prime instance of a really collaborative spirit with a shared imaginative and prescient: to develop modern therapies that concentrate on RAS-driven cancers with precision and efficacy to present new hope to most cancers sufferers,” stated LLNL’s Yue Yang, a computational chemist and a lead researcher on the challenge. “We need to thank BridgeBio for trusting us to grow to be a part of their crew, and to have an effect on future candidates in addition to their ongoing drug discovery efforts. BridgeBio’s willingness to combine us with their plans was key to the success of this drug.”
Yang added that the LCADD platform used to find BBO-8520 is broad and customizable to a variety of illnesses, together with different types of most cancers and infectious illness. By collaborating with U.S. trade, scientists may check and enhance the platform to fight future organic threats with the peace of mind of a validated system.
The work leverages computational drug design capabilities initially motivated by a DOE-NCI partnership beneath the Most cancers Moonshot, which goals to use world-class computing assets at LLNL and different DOE nationwide laboratories to advance most cancers analysis and therapy for the general public good. Researchers on the challenge stated the partnership’s success in growing a tangible drug candidate underscores the worth of uniting experience from the DOE nationwide laboratories, biomedical analysis establishments and modern corporations to resolve tough challenges resembling most cancers. It additionally signifies the computational method may save thousands and thousands of {dollars} and beneficial time — maybe years — over the standard drug discovery course of, the place even promising compounds can fail earlier than reaching human testing.
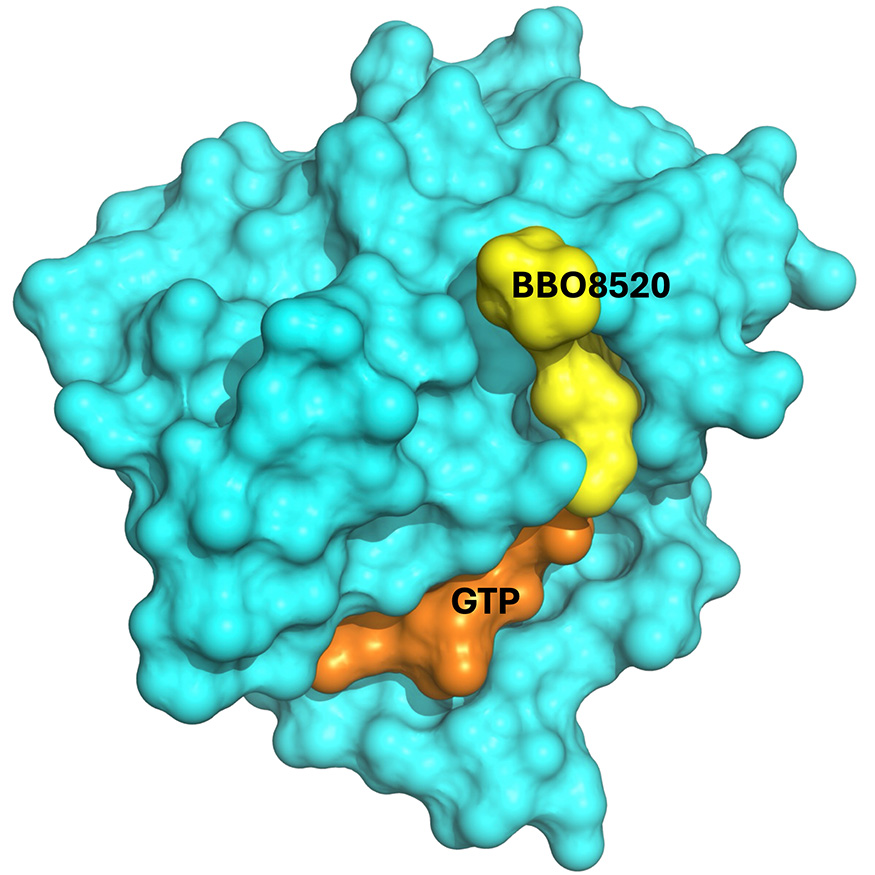
It is a floor illustration of the interplay among the many most cancers drug candidate, BBO-8520 (yellow), the pure substrate guanosine triphosphate (or GTP, orange) and a KRAS protein (cyan). Picture by LLNL.
“By means of our collaboration with LLNL and FNL, we’ve reached a major achievement in drug discovery for inhibiting KRAS mutations that result in most cancers,” stated BridgeBio Oncology Therapeutics Chief Science Officer Pedro Beltran. “The event of BBO-8520 may solely have been potential by means of our partnership method and exemplifies the facility of teamwork and innovation. This drug was capable of attain human trials in report time and epitomizes the potential of computational and AI-enabled drug design to save lots of time, cash and lab assets on new drug discovery. It’s a testomony to the intense way forward for our collaboration and the hope it could possibly carry to sufferers in want. We’re proud to proceed working alongside LLNL and FNL to push the boundaries of what’s potential in most cancers analysis.”
Along with advancing most cancers analysis, LLNL representatives stated the milestone is validation that integrating supercomputing with AI-and physics-based computational platforms has the potential to additional speed up small molecule drug discovery and equip DOE, the Nationwide Nuclear Safety Administration and LLNL with the power to rapidly and routinely develop medical countermeasures for illness or future pandemics, aligning with broader mission focus areas in biosecurity, bio-resilience and nationwide safety.
“By means of this pioneering partnership, LLNL, the Frederick Nationwide Laboratory for Most cancers Analysis and BridgeBio have unlocked a beacon of optimism within the struggle towards most cancers—and that is solely the start of what we hope can be an extended and fruitful collaboration,” stated Pat Falcone, Deputy Director for Science and Expertise at LLNL. “This fast journey from computational simulations to human trials for this drug displays the transformative energy of analysis on the DOE nationwide laboratories and ensures we’re higher ready for the subsequent pandemic. This collaboration stands as a testomony to the potential of public-private partnerships, and we invite different establishments and firms to affix us within the pursuit of modern options by means of computational and AI-aided drug design. Collectively, we have now accelerated the tempo of discovery.”
Preliminary analysis and funding for the work got here from the RAS Initiative, established by NCI to discover novel approaches to assault proteins encoded by mutant types of RAS genes and to finally create efficient, new therapies for RAS-related cancers. Amongst all types of RAS proteins, KRAS is essentially the most desired goal for therapeutic therapy due to the prevalence of mutant (oncogenic) KRAS in pancreatic, lung and colorectal most cancers, researchers stated. Mutations of the RAS household of genes are implicated in 20-30 % of all cancers — together with 95 % of pancreatic cancers and 45% of colorectal cancers.
“The Frederick Nationwide Laboratory’s longstanding relationships with our colleagues at Lawrence Livermore by means of the NCI-DOE collaboration set the stage for this public-private partnership with BridgeBio which represents a definite mannequin for drug improvement that encompasses world-class computing capabilities,” stated Dwight Nissley, most cancers biologist and head of the RAS Initiative crew at FNL. “By leveraging every companion’s distinctive strengths, we realized a long-standing aim of the NCI, to develop novel therapeutic choices for RAS-driven cancers.”
Usually, RAS proteins obtain and observe alerts to modify between energetic and inactive states. Like a light-weight change, mutated RAS proteins resembling KRASG12C can grow to be caught in an “at all times on” state that causes cells to develop uncontrolled; forming tumors and the most cancers itself to unfold to different elements of the physique. Whereas current drug therapies goal to show this change off, cancerous cells generally nonetheless discover methods to show it again on once more — making the therapies much less efficient over time. In contrast to most present KRASG12C medicine, BBO-8520 targets KRASG12C in each its energetic and inactive states, successfully blocking its operate and hindering most cancers development. This twin mechanism is believed to supply benefits over current therapies by addressing some mechanisms of resistance that may develop over time.
Preclinical research demonstrated promising outcomes for BBO-8520, displaying statistically important inhibition of tumor development in varied most cancers fashions, even in instances the place resistance has emerged towards different drugs concentrating on the identical protein. By binding solely to the “off” conformation, current therapies “lead to a affected person growing resistance fairly rapidly,” leading to most cancers development, stated Anna Maciag, a most cancers biochemist who led the FNL’s preclinical work on BBO-8520. “This twin inhibitor hits the ‘on’ and ‘off’ states concurrently, offering 100% protection of the goal,” Maciag added.
The research counsel that BBO-8520 has the potential to be simpler in treating sure forms of most cancers, significantly these pushed by mutations within the KRASG12C gene, which performs a vital position in most cancers cell development and proliferation and for many years has been thought of undruggable by the scientific group.
LLNL Innovation and Partnerships Office (IPO) Enterprise Growth Government Yash Vaishnav negotiated the CRADA with BridgeBio subsidiary Theras, in addition to the license settlement for the drug candidate with BridgeBio Oncology Therapeutics. Vaishnav additionally manages the mental property portfolio of KRAS inhibitors developed beneath the CRADA and the connection along with his counterparts at BridgeBio. IPO is the focus for LLNL’s engagement with trade and goals to speed up U.S. competitiveness by figuring out new financial alternatives and options and transferring these to the non-public sector by means of licensing or partnerships.
supply: Jeremy Thomas, Lawrence Livermore Nationwide Laboratory
1.png)








