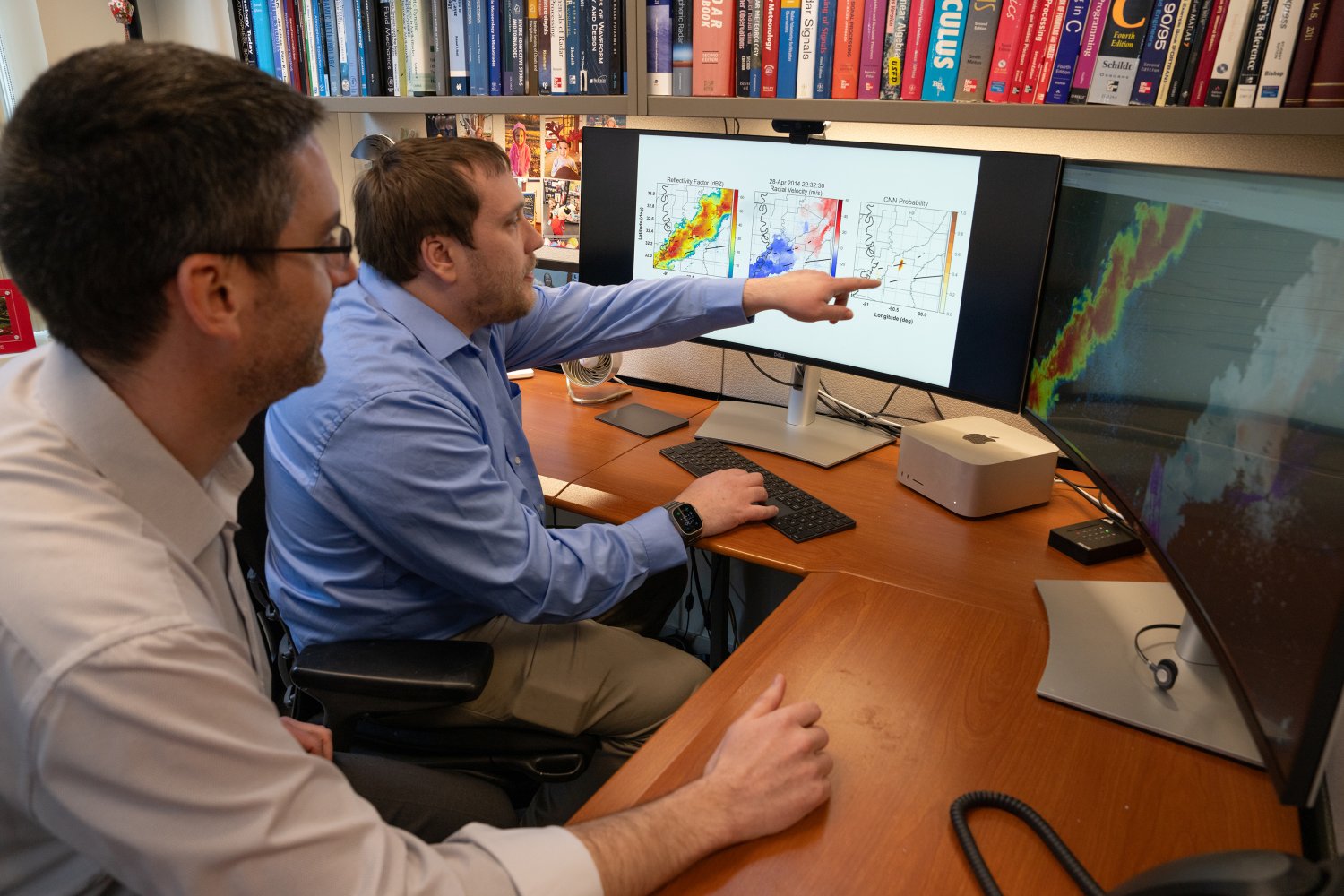
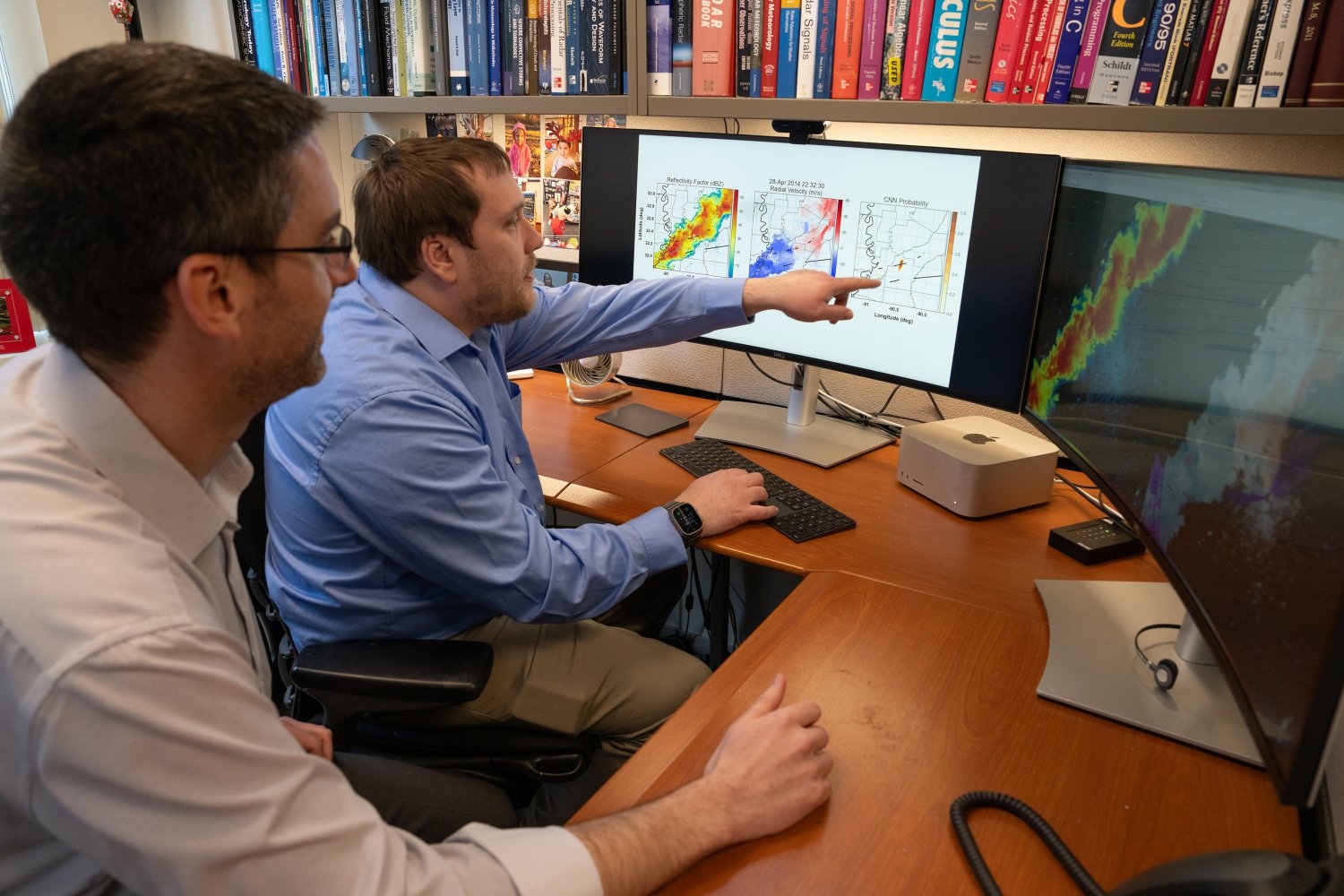
The return of spring within the Northern Hemisphere touches off twister season. A twister’s twisting funnel of mud and particles appears an unmistakable sight. However that sight could be obscured to radar, the software of meteorologists. It is onerous to know precisely when a twister has fashioned, and even why.
A brand new dataset may maintain solutions. It accommodates radar returns from hundreds of tornadoes which have hit america prior to now 10 years. Storms that spawned tornadoes are flanked by different extreme storms, some with practically similar situations, that by no means did. MIT Lincoln Laboratory researchers who curated the dataset, referred to as TorNet, have now launched it open supply. They hope to allow breakthroughs in detecting certainly one of nature’s most mysterious and violent phenomena.
“Loads of progress is pushed by simply accessible, benchmark datasets. We hope TorNet will lay a basis for machine studying algorithms to each detect and predict tornadoes,” says Mark Veillette, the venture’s co-principal investigator with James Kurdzo. Each researchers work within the Air Site visitors Management Techniques Group.
Together with the dataset, the group is releasing fashions educated on it. The fashions present promise for machine studying’s capacity to identify a tornado. Constructing on this work may open new frontiers for forecasters, serving to them present extra correct warnings that may save lives.
Swirling uncertainty
About 1,200 tornadoes happen in america yearly, inflicting thousands and thousands to billions of {dollars} in economic damage and claiming 71 lives on common. Final 12 months, one unusually long-lasting tornado killed 17 individuals and injured no less than 165 others alongside a 59-mile path in Mississippi.
But tornadoes are notoriously tough to forecast as a result of scientists do not have a transparent image of why they kind. “We are able to see two storms that look similar, and one will produce a twister and one will not. We do not absolutely perceive it,” Kurdzo says.
A twister’s primary components are thunderstorms with instability brought on by quickly rising heat air and wind shear that causes rotation. Climate radar is the first software used to watch these situations. However tornadoes lay too low to be detected, even when reasonably near the radar. Because the radar beam with a given tilt angle travels farther from the antenna, it will get increased above the bottom, principally seeing reflections from rain and hail carried within the “mesocyclone,” the storm’s broad, rotating updraft. A mesocyclone would not at all times produce a twister.
With this restricted view, forecasters should resolve whether or not or to not problem a twister warning. They typically err on the facet of warning. In consequence, the speed of false alarms for twister warnings is greater than 70 p.c. “That may result in boy-who-cried-wolf syndrome,” Kurdzo says.
In recent times, researchers have turned to machine studying to raised detect and predict tornadoes. Nonetheless, uncooked datasets and fashions haven’t at all times been accessible to the broader group, stifling progress. TorNet is filling this hole.
The dataset accommodates greater than 200,000 radar pictures, 13,587 of which depict tornadoes. The remainder of the pictures are non-tornadic, taken from storms in certainly one of two classes: randomly chosen extreme storms or false-alarm storms (those who led a forecaster to problem a warning however that didn’t produce a twister).
Every pattern of a storm or twister includes two units of six radar pictures. The 2 units correspond to completely different radar sweep angles. The six pictures painting completely different radar information merchandise, corresponding to reflectivity (exhibiting precipitation depth) or radial velocity (indicating if winds are transferring towards or away from the radar).
A problem in curating the dataset was first discovering tornadoes. Inside the corpus of climate radar information, tornadoes are extraordinarily uncommon occasions. The group then needed to stability these twister samples with tough non-tornado samples. If the dataset have been too straightforward, say by evaluating tornadoes to snowstorms, an algorithm educated on the information would seemingly over-classify storms as tornadic.
“What’s stunning a few true benchmark dataset is that we’re all working with the identical information, with the identical degree of issue, and might examine outcomes,” Veillette says. “It additionally makes meteorology extra accessible to information scientists, and vice versa. It turns into simpler for these two events to work on a typical drawback.”
Each researchers signify the progress that may come from cross-collaboration. Veillette is a mathematician and algorithm developer who has lengthy been fascinated by tornadoes. Kurdzo is a meteorologist by coaching and a sign processing knowledgeable. In grad college, he chased tornadoes with custom-built cellular radars, amassing information to investigate in new methods.
“This dataset additionally signifies that a grad pupil would not must spend a 12 months or two constructing a dataset. They’ll bounce proper into their analysis,” Kurdzo says.
This venture was funded by Lincoln Laboratory’s Climate Change Initiative, which goals to leverage the laboratory’s numerous technical strengths to assist handle local weather issues threatening human well being and world safety.
Chasing solutions with deep studying
Utilizing the dataset, the researchers developed baseline synthetic intelligence (AI) fashions. They have been significantly keen to use deep studying, a type of machine studying that excels at processing visible information. By itself, deep studying can extract options (key observations that an algorithm makes use of to decide) from pictures throughout a dataset. Different machine studying approaches require people to first manually label options.
“We wished to see if deep studying may rediscover what individuals usually search for in tornadoes and even determine new issues that usually aren’t looked for by forecasters,” Veillette says.
The outcomes are promising. Their deep studying mannequin carried out much like or higher than all tornado-detecting algorithms identified in literature. The educated algorithm appropriately categorized 50 p.c of weaker EF-1 tornadoes and over 85 p.c of tornadoes rated EF-2 or increased, which make up probably the most devastating and dear occurrences of those storms.
Additionally they evaluated two different varieties of machine-learning fashions, and one conventional mannequin to match towards. The supply code and parameters of all these fashions are freely accessible. The fashions and dataset are additionally described in a paper submitted to a journal of the American Meteorological Society (AMS). Veillette offered this work on the AMS Annual Assembly in January.
“The largest cause for placing our fashions out there may be for the group to enhance upon them and do different nice issues,” Kurdzo says. “One of the best resolution could possibly be a deep studying mannequin, or somebody may discover {that a} non-deep studying mannequin is definitely higher.”
TorNet could possibly be helpful within the climate group for others makes use of too, corresponding to for conducting large-scale case research on storms. It is also augmented with different information sources, like satellite tv for pc imagery or lightning maps. Fusing a number of varieties of information may enhance the accuracy of machine studying fashions.
Taking steps towards operations
On high of detecting tornadoes, Kurdzo hopes that fashions may assist unravel the science of why they kind.
“As scientists, we see all these precursors to tornadoes — a rise in low-level rotation, a hook echo in reflectivity information, particular differential section (KDP) foot and differential reflectivity (ZDR) arcs. However how do all of them go collectively? And are there bodily manifestations we do not find out about?” he asks.
Teasing out these solutions is likely to be attainable with explainable AI. Explainable AI refers to strategies that enable a mannequin to supply its reasoning, in a format comprehensible to people, of why it got here to a sure resolution. On this case, these explanations may reveal bodily processes that occur earlier than tornadoes. This data may assist prepare forecasters, and fashions, to acknowledge the indicators sooner.
“None of this expertise is ever meant to interchange a forecaster. However maybe sometime it may information forecasters’ eyes in complicated conditions, and provides a visible warning to an space predicted to have tornadic exercise,” Kurdzo says.
Such help could possibly be particularly helpful as radar expertise improves and future networks doubtlessly develop denser. Information refresh charges in a next-generation radar community are anticipated to extend from each 5 minutes to roughly one minute, maybe quicker than forecasters can interpret the brand new data. As a result of deep studying can course of big quantities of information shortly, it could possibly be well-suited for monitoring radar returns in actual time, alongside people. Tornadoes can kind and disappear in minutes.
However the path to an operational algorithm is a protracted highway, particularly in safety-critical conditions, Veillette says. “I feel the forecaster group remains to be, understandably, skeptical of machine studying. One solution to set up belief and transparency is to have public benchmark datasets like this one. It is a first step.”
The subsequent steps, the group hopes, shall be taken by researchers internationally who’re impressed by the dataset and energized to construct their very own algorithms. These algorithms will in flip go into check beds, the place they’re going to ultimately be proven to forecasters, to start out a technique of transitioning into operations.
In the long run, the trail may circle again to belief.
“We could by no means get greater than a 10- to 15-minute twister warning utilizing these instruments. But when we may decrease the false-alarm price, we may begin to make headway with public notion,” Kurdzo says. “Individuals are going to make use of these warnings to take the motion they should save their lives.”









